Cooling towers are remarkable structures that play a vital role in maintaining optimal operating conditions for various industrial processes, power plants, and HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems. These انواع برج خنک کننده edifices are not just symbols of industrial landscapes but are indispensable components contributing to energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Understanding the Functionality:
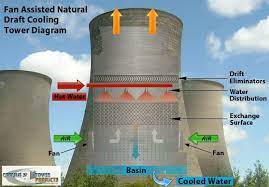
At its core, a cooling tower is a heat rejection device that transfers waste heat from processes to the atmosphere through the process of evaporation. This is achieved by circulating water through the tower and allowing a small portion of it to evaporate, thereby releasing heat into the air. The cooled water is then recirculated back into the system, ready to absorb more heat.
Types of Cooling Towers:
There are several types of cooling towers, each designed to suit specific applications and operating conditions:
- Natural Draft Cooling Towers: These towers utilize the stack effect, where warm air rises and cool air is drawn in through the tower’s openings. They are often used in large power plants and industrial facilities due to their high capacity and efficiency.
- Mechanical Draft Cooling Towers: Unlike natural draft towers, mechanical draft towers use fans to draw air through the tower, enhancing heat exchange efficiency. They are more versatile and can be tailored to suit varying cooling requirements.
- Crossflow and Counterflow Cooling Towers: These classifications refer to the arrangement of airflow relative to the direction of water flow within the tower. Crossflow towers feature airflow perpendicular to the water flow, while counterflow towers have airflow opposing the water flow. Each design has its advantages and is chosen based on factors such as space availability and efficiency requirements.
Applications Across Industries:
Cooling towers find widespread use across diverse industries:
- Power Generation: In power plants, cooling towers play a critical role in dissipating the excess heat generated during electricity production. Whether in nuclear, coal-fired, or natural gas power plants, cooling towers are essential for maintaining thermal efficiency and environmental compliance.
- Manufacturing: Industrial processes such as steel production, chemical manufacturing, and petroleum refining generate substantial heat that must be efficiently removed to ensure equipment longevity and product quality. Cooling towers provide an effective means of heat dissipation in these applications.
- Commercial HVAC Systems: Large commercial buildings, such as office complexes and shopping malls, rely on cooling towers as part of their HVAC systems to regulate indoor temperatures. By efficiently removing heat from circulating water, cooling towers help maintain comfortable environments while minimizing energy consumption.
Advancements and Environmental Considerations:
In recent years, there has been a significant focus on enhancing the efficiency and environmental sustainability of cooling towers. Advancements in materials, design, and control systems have led to more energy-efficient operations and reduced water consumption.
Moreover, technologies such as hybrid cooling systems, which combine the benefits of evaporative cooling with dry cooling methods, offer further opportunities for improving efficiency and water conservation.
Additionally, the use of alternative cooling fluids, such as glycol or ammonia, in place of water in certain applications helps mitigate water scarcity concerns and reduces environmental impact.
Conclusion:
Cooling towers are indispensable assets in modern industrial and commercial settings, playing a crucial role in maintaining process efficiency and environmental sustainability. As industries continue to prioritize energy efficiency and environmental responsibility, the ongoing evolution of cooling tower technologies will remain pivotal in meeting these objectives. From towering giants on the industrial skyline to discreet installations within urban landscapes, cooling towers silently uphold the foundations of modern infrastructure, ensuring the seamless functioning of essential processes while minimizing their environmental footprint.