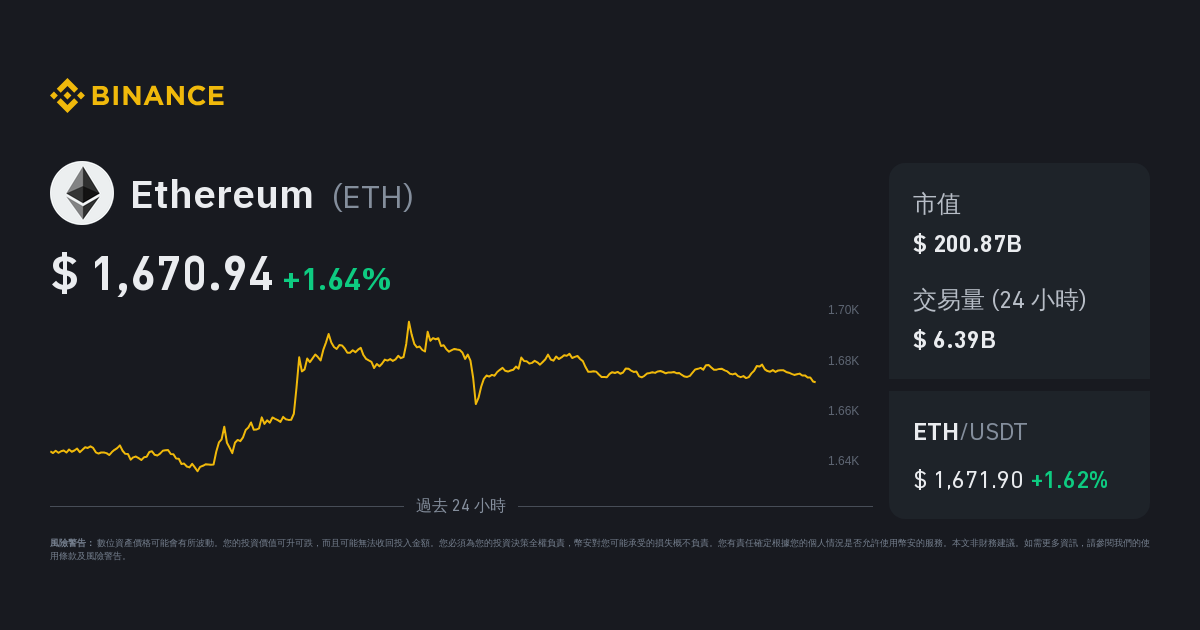
In the realm of blockchain technology, 以太幣價格 stands as a pioneering force that has redefined possibilities for decentralized applications and smart contracts. Launched in 2015 by visionary programmer Vitalik Buterin, Ethereum introduced a groundbreaking concept that extended the capabilities of blockchain beyond mere transactions. At its core lies the Ethereum Virtual Machine
(EVM), a decentralized computing environment enabling the execution of smart contracts – self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. This innovation has given rise to a plethora of use cases across industries.The driving force behind Ethereum’s versatility is its ability to foster the development of decentralized applications (DApps).
These applications operate on a network of computers rather than a single server, ensuring transparency, security, and censorship resistance. DApps have found applications in domains as diverse as finance, supply chain management, gaming, and more. Notably, the world of decentralized finance (DeFi) has flourished on the Ethereum platform, revolutionizing traditional financial services through concepts like decentralized lending, automated trading, and yield farming.
Ethereum’s journey has not been without challenges. The network’s scalability and high gas fees have been subjects of concern, particularly during periods of high demand. In response, Ethereum has been undergoing a transition from a Proof of Work (PoW) to a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism as part of Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. This upgrade aims to enhance scalability, security, and sustainability while reducing the environmental impact associated with PoW mining.
The Ethereum community is a dynamic ecosystem of developers, enthusiasts, and innovators. This community has birthed a myriad of projects, each contributing to Ethereum’s growth and improvement. Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) serve as a means for proposing changes and upgrades to the network, promoting a collaborative approach to decision-making.